How soon after knee replacement can I use exercise bike?
You can start using an exercise bike within the first 48-hours following a knee replacement surgery.
Standard practice in many physical therapy clinics is to begin using a recumbent bike with a gentle rocking motion until the knee is capable of a completing full rotation without significant pain.
When is it recommended to start using a stationary bike following a total knee replacement?
Immediately following the procedure a physical therapist will ensure the patient is safe to stand, walk, and move around the recovery room.
Many total knee replacements are performed on an outpatient basis and patients are discharged to home the same day.
A physical therapist or your surgeon may recommend you start using an exercise bike within 48-hours following surgery to keep the knee moving and reduce the chances of blood clots.
* Recommendation: when a stationary bike is used in the early recovery stages it is often recommended that the patient start with pedal rocks until the knee is capable of a full revolution without significant pain or compensation.
Phase 1 – Week 1 Post Op:
During the first week following knee replacement surgery a recumbent bike is often used to initiate joint motion.
Pedal rocks are an exercise used in which you place both feet on the pedals of the bike with the surgical knee foot on the lower pedal. You gently rock the pedals forward and back to initiate movement at the knee joint without significant pain.
Pedal rocks are performed for 3 to 5 minute episodes or as tolerated by the patient.
This exercise is usually performed 3 times a day if you have access to a recumbent or upright exercise bike at home.
As your range of motion improves you increase the size of the arcing motion until a full pedal revolution is achieved.
* TIP: Some patients prefer a reverse revolution at first until the knee range of motion has improved enough to complete a forward revolution.
Phase 2 – Week 2-4 Post Op:
As time on the exercise bike increases to 10-minutes the next phase would be to increase time walking and performing other exercises on your feet.
Once you can perform a 10-minute episode of pedaling on the exercise bike then spending more time performing weight bearing exercises are encouraged.
Some examples of weight bearing exercises include the following:
- Walking
- Elliptical Trainer
- Stairs
- Treadmill
- Stair Stepper
Phase 3 – Weeks 5-12 Post Op:
After 10-minutes of continuous cycling has been achieved, consider increasing the resistance and intensity of the time spent on an exercise bike.
Intensity may be varied by increasing the speed, moving the seat closer to the pedals to gain more range of motion, or increasing the resistance.
Interval training is another great option for increasing the intensity of time spent on an exercise bike.
A sample program may look like the following:
2-minutes warming up at a comfortable pace and seat position
2-minutes of 4 rounds of (10-seconds light resistance high speed | 20-seconds of light resistance low speed)
2-minutes of 4 rounds of (10-seconds high resistance low speed | 20-seconds of light resistance low speed)
2-minutes of high resistance low speed with a seat position close to the pedals
2-minutes cool down at a comfortable pace and seat position
What kind of stationary bike is recommended following a total knee replacement?
There are 4 common types of stationary bike:
1.) A recumbent bike – This is a bike that has a larger seat and back rest attached to the seat. The pedals are more forward and the seat level is closer to pedal level. See this post for more details >
2.) An upright bike – This bike has a smaller seat, no back support, and the seat is typically positioned above the pedals.

Upright-Stat-Bike-TKR-Rehab
3.) A fan bike – This is usually a version of an upright bike. It has arms that move in conjunction with the foot pedals and uses air resistance.
4.) Budget pedaler – This is a small, light weight pedal device that may be placed infront of a chair. The device is usually priced at less than $50. This device is often used for the lower body while sitting and the upper body while standing.
* Recommendation: when choosing any piece of exercise equipment the most important consideration is use… ‘Will You Use It?’
Buy something you will use. Buy something you will enjoy. Buy something that will improve your quality of life.
What if I cannot complete a full revolution on the pedals?
This video shares a simple strategy to start using a recumbent bike even if your knee flexion is limited.
* Recommendation: Unhook the strap on the pedal of your surgical side leg. Position your heel on the pedal on your surgical side leg while placing the ball of the foot on the center of the pedal on your non-surgical leg. Gently rock the pedals back and forth until you are able to complete a full revolution. Repeat the as the knee motion improves and move your seat slowly forward as tolerated.
What can I do to relax my thigh muscle?
A common report from patients is that the thigh muscle, the quadriceps, will tighten up as soon as they try to complete a full revolution on a bike.
That can happen for several reasons, but the most common is due to the body’s natural protective response. When something hurts or has the potential to hurt our body will tighten the muscles around a joint to prevent movement and prepare for pain.
One way to reduce this response is to massage the muscle. My favorite is a rolling pin massage. In this video you can see how a simple rolling pin from the kitchen will reduce pain, reduce guarding, and improve tissue mobility.
More Blog Posts …
What causes sciatica after knee replacement?
Occasionally after a total knee replacement, my patients reports signs and symptoms consistent with sciatica. My patients describe a sharp, burning hot poker stabbing them in the buttock with searing pain that runs down the lateral back of the leg to the knee and...
Top 3 Devices To Help Get An Elderly Person Up From The Floor
3 Best Devices in 2021 To Help An Elderly Person UP from the Floor After a Fall. Under $100, Under $1,000, and Over $2,000
Lymphedema LIVE Class Registration
WHAT: In this LIVE class you will learn what you can do to manage swelling, reduce pain, and improve healing after a total knee replacement surgery. Dr. Andrea Leifer, PT, CLT-LANA is a lymphedema expert and educator. WHEN: March 31, 2021 at 3PM EST WHERE: Online Zoom...
10 Questions About Leg Elevation After Knee Surgery
Physical Therapist Anthony Maritato, PT Recommends the 3 BEST leg elevation pillows after knee replacement surgery | 10 Common Questions Patients Ask
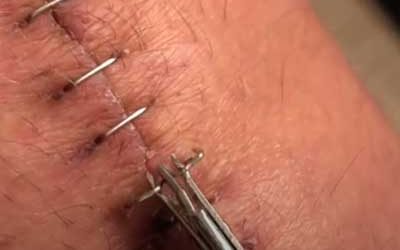
Does It Hurt To Have Staples Removed After Knee Replacement Surgery
Removing Staples After Knee Replacement Surgery Staple removal is often painless and quick. In the following video a person removes his staples at home, but it is always recommended you allow your physician or surgical team remove the staples in their office.Why Are...
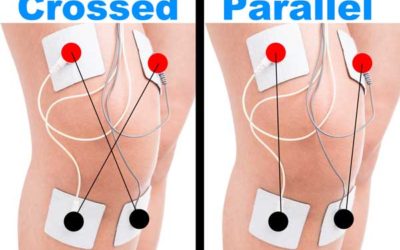
BEST Tens Placement for Knee Pain
Is TENS a Good Way to Reduce Knee Pain? Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) is a non-invasive, drug-free method for pain relief that has been widely used to manage various types of pain, including knee pain. TENS therapy involves sending low-voltage...
How many times a day can you do Neck Traction
Neck (cervical) traction is most commonly prescribed in 10 to 20 minute episodes. In this article I share the BEST positions to use cervical traction and what you NEED to AVOID when using it.
Which Activities Should I Avoid After Total Knee Replacement?
Click here to see a list of activities you should avoid after total knee replacement as well as a BUNCH of activities you may ENJOY.
Why Does my Knee Replacement Make Noise?
Would you like to know why your knee replacement makes noise? Is it a grinding? Is it a clicking? Or is it a popping? Snap, crackle, pop may be common after a total knee replacement. Read on to learn why-
How long should I ICE my knee after knee replacement?
Icing after a total knee replacement should be performed for between 10 and 20-minutes. If icing is painful then consider using heat instead. Explore myths about icing in this article.